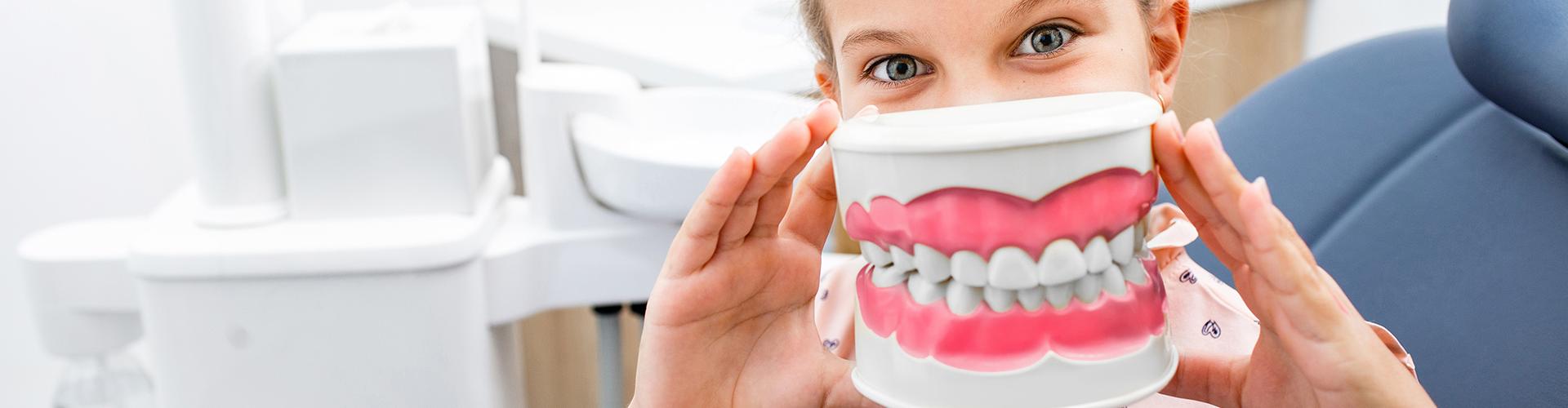
Pediatric dentistry is a science dealing with the dental and oral diseases (and their prevention) of children. Many people are not aware, but the importance of pediatric dentistry is much higher than we would assume, because pediatric dental treatments can determine children’s attitude towards dental health and treatments for their whole life.
About the importance of baby teeth
The human body develops two sets of teeth. The first set, the so called baby teeth (temporary teeth, dentes decidui) start to appear six months after birth, the permanent teeth (dentes permanentes) after six years of age. The development of teeth starts at the 7th week of embryonic life, when the baby’s body is “building” teeth. In order to create healthy teeth the baby requires calcium, phosphorus and a combination of other minerals and vitamins. The growth of baby teeth happens between the 6th and 14th months, but all 20 baby teeth are partially developed before birth.
Baby teeth have an important role in the development of correct bite and mastication, as well as the development of correctly making speech sounds. They also act as placeholders for the permanent teeth. The teeth are only considered completely permanent after the last baby of the teeth is lost. Permanent teeth appear in order of their place in the jaws.
About children’s preventive dental care
In dental care, it is very important to prevent dental problems, this is known as preventive care. The aim of preventive care is to inhibit the diseases and harmful conditions of the mouth and the
Children’s teeth are primarily healthy. The future fate of these intact teeth is mainly the parents’ responsibility, as it is the parents’ duty to teach their kids how important it is to keep their teeth healthy. It is critical that parents take their children to the dentist 3 or 4 times a year, starting from as young an age as 2-3 years. It is advisable that parents take their children to see a dentist at least every 6 months to check on their teeth, because this allows for the early recognition and effective treatment of any potential problems, and also provides an opportunity to receive advice about how to maintain a good dental care habit.
Many parents believe that the decay of baby teeth is only a temporary problem, because the child will lose them eventually anyway. This, however, is an incorrect notion, because a decayed tooth may cause the child pain, and the premature loss of baby teeth alters the position of the erupting permanent teeth. This is why regular screening is very important - if the decay is noticed in time it can be treated without extracting the affected temporary tooth.
About the treatment of temporary teeth
The structure of baby teeth is different than those of permanent teeth: the pulp chambers are much bigger, and the enamel is thinner, so tooth decay can happen faster, but symptoms are identical to those of permanent teeth, and may cause the child pain.
The treatment of baby teeth can happen with or without anesthesia, depending on the size of the problem. In case only a small area is affected by the decay it is much easier to remove, as it is enough to shave and varnish the affected tooth.
The procedure of filling baby teeth starts with making the decayed area easily cleanable by drilling, then inserting the filling material into the tooth - it isn’t always necessary to use anesthesia during these procedures. As part of the procedure, a special material (glass ionomer cement) is inserted into the tooth to serve as a ‘fluoride depository’, protecting the baby tooth until exfoliation, as the filling of baby teeth need to last as long as the teeth themselves stay in the mouth.
In case of severe decay, inflammation, or dead teeth an extraction may be necessary. Baby teeth can usually be extracted quickly, as they are only held in place by the gums. This makes it possible to only use Lidocaine spray as a local anesthetic for this procedure in most cases.
If cavities are left untreated, the situation can turn so severe that the nerve becomes inflamed, causing the child a considerable amount of pain. Baby teeth’s root canals cannot be treated in the same way as permanent teeth, so a special ‘mummifying’ paste is often used - this seeps into the root canal, conserving and keeping the nerve sterile. This procedure can help end the pain and ensure the absorption of the root, which is necessary for the loss of primary teeth.
Fissure sealing
Dental fissure sealing is a simple, quick, cheap, pain-free and aesthetically pleasing way to prevent decay on the surface of the molars. The procedure is relatively simple, only takes a few minutes per teeth, and isn’t taxing on the patient. The sealing of fissures in the tooth surface ensures that food cannot get stuck in the fissures, making the appearance of decay less likely.
The treatment is applicable between the ages of 6 and 18, and it is advised to close fissures on newly erupted teeth during the biannual checkups, as well as to check on previously sealed fissures and change the sealant if necessary. This procedure can help prevent, or largely decrease the appearance of tooth decay in children.